Mobile phone antenna and its design key points
The antenna in a mobile phone: The antenna is a core component of a mobile phone and should be given special attention. In actual production, there are often cases where the antenna indicators do not meet the requirements, leading to project failure.
一、The evolution of antenna forms:
The earliest mobile phones had external antennas. NOKIA began to use built-in antennas, which were made of metal sheets (usually 0.1MM thick stainless steel sheets formed by stamping). Later, to reduce costs, FPC was adopted as a substitute. The characteristics of FPC are that it is soft in material, can be attached to curved surfaces, and can also be turned. In terms of space utilization, it has an advantage over metal. The requirements for the shape design and structural design are higher than those for metal free points. When assembling FPC, it only needs to be attached to the material surface, but positioning columns need to be added at the feed points. Unlike metals, which require heating and positioning of the molten column. It is the mainstream antenna technology at present. Later, with the development of technology, the LDS antenna technology was developed. It is to directly engrave the antenna on specially treated materials with a laser. This technology is widely used in current high-end mobile phones, usually on the main antenna, and is made together with the speaker box to save costs.
二、Other antennas on mobile phones:
Besides the main antenna (3G/4G network), there are other antennas on mobile phones. Commonly used ones include GPS positioning antennas, BT/WIFI antennas, NFC antennas, FM (radio) antennas, etc. One type of GPS antenna is a dedicated ceramic antenna with various specifications. Dedicated antennas have good performance, but they are relatively large in size and difficult to handle in shape. They are difficult to use in high-end mobile phones or thinner mobile phones. Generally, FPC is still used. BT/WIFI is usually FPC as well, but some low-end mobile phones also use a cable instead. NFC antennas are used for mobile FM antennas. In some elderly mobile phones, they still exist separately, usually as a telescopic antenna. On ordinary mobile phones, headphone cables are used instead (so headphones must be used when listening to the radio). The following several pictures show different forms of antennas:
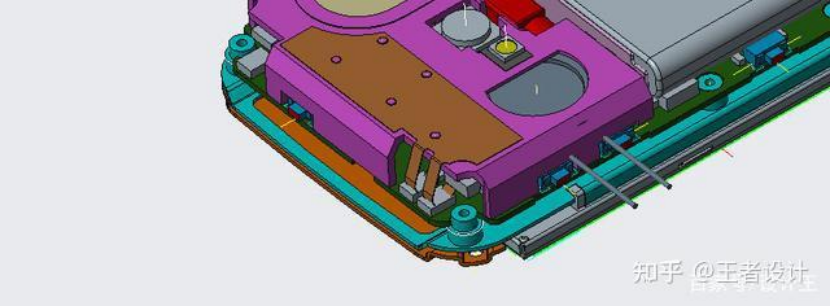
Figure1:The positioning column can be seen in the metal antenna diagram in Figure 1
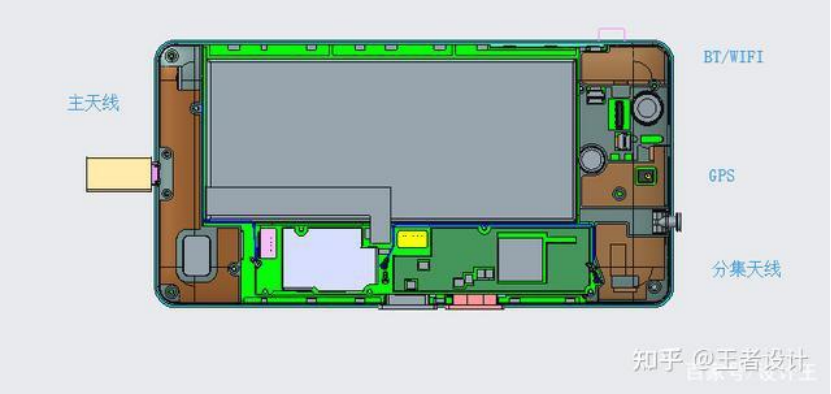
Figure 2: Main antennas and their positions on FPC antenna mobile phones
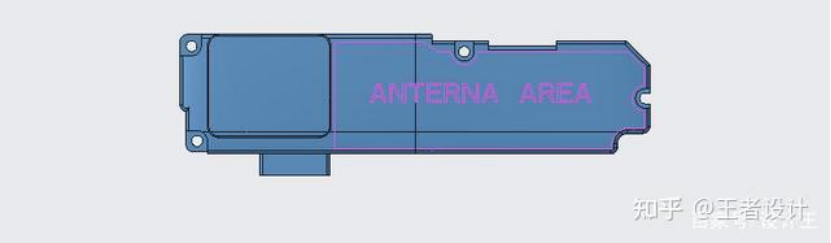
Figure3: The engraved area is given in the LDS antenna diagram in Figure 3
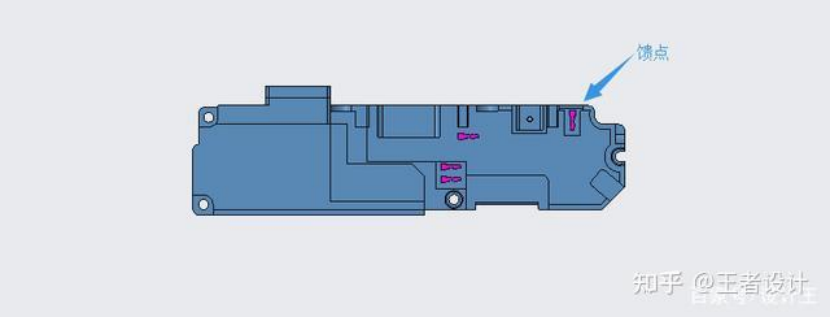
Figure 4: Back of the LDS antenna
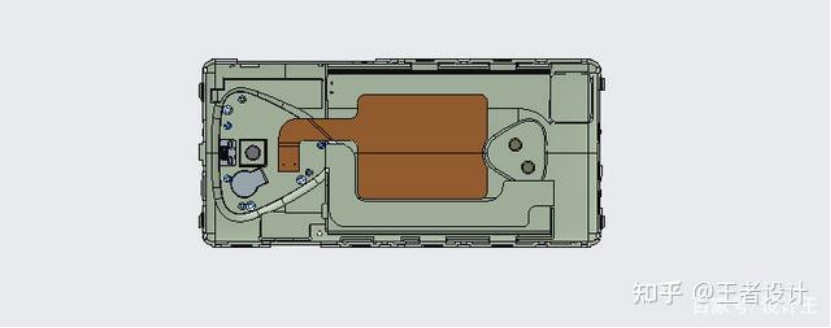
Figure 5: NFC Antenna

Figure 6: shows the physical pictures of LDS online
三、Key points of the three-antenna structure:
An important parameter of an antenna is its area, especially for the main antenna. The general data for 3G networks is 400MM ², while for 4G networks, it is generally required to reach 500MM ². This is because to be backward compatible with 2G and 3G networks, such a large area is usually difficult to guarantee, so it is often necessary to use the side or metal frame. Generally, 4G antennas (especially those for full network compatibility) are usually difficult to adjust. Before and after the design, they need to be evaluated by the antenna factory, and the design should be based on the factory's opinions. Some may need to be modified several times to achieve the desired effect. The safe distance between the two antennas and other periods must be at least 1 millimeter. It is best that there are no electromagnetic devices or lines that require signal transmission near the three antennas, as these will interfere with each other. Generally, companies require that the antenna be 5 millimeters away from the mainboard, but this is usually not achievable. However, the minimum distance should not be less than 2 millimeters. For mobile phones with metal frames, it is required that the metal frame be 2 millimeters away from the antenna.
四、Antenna design:
There are generally two installation positions for the antenna. One is a separate bracket, which is locked on the motherboard or the front shell, and the FPC is attached to the bracket. The other is attached to the back shell. The thickness of the FPC is 0.15 millimeters. During the design process, the sink platform is first made at the corresponding location with a depth of 0.3 millimeters. Then, the FPC is drawn at the sink platform position. Usually, a solid surface is generated, and the feed point range is marked at the PIN. A reinforcing plate is added to the back, typically a steel sheet 0.1 to 0.2 thick, along with one or two positioning columns. After drawing, check the position, especially the feed point range should align with the shrapnel or PIN on the upper board. The following picture is an example involving a good NFC antenna:
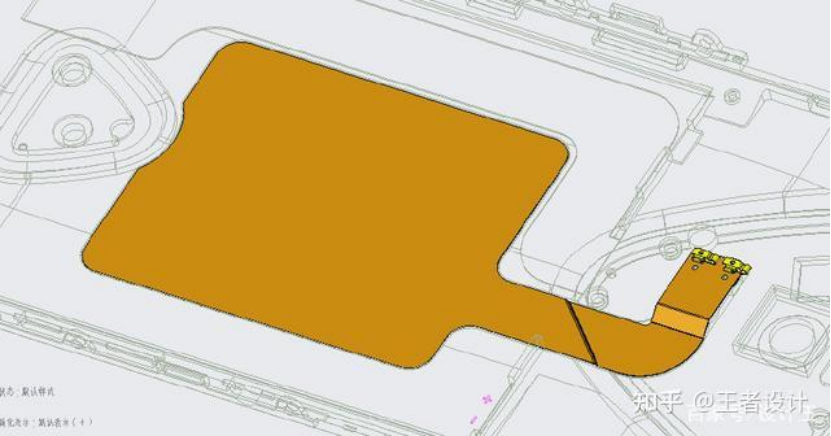
Figure 7: NFC antenna when completed

