Modern smartphones rely on various antenna technologies to enable wireless communication. As 5G networks and compact device designs evolve, understanding different antenna types becomes crucial. Here's our comprehensive guide:
1. PCB Trace Antennas
Structure:
Etched copper traces directly on the phone's printed circuit board
Advantages:
✓ Lowest production cost
✓ Easy integration with RF circuits
✓ Compact footprint
Disadvantages:
✗ Limited frequency bandwidth
✗ Susceptible to interference
✗ Difficult to modify post-production
Common Use: Basic WiFi/BT connectivity in budget devices.
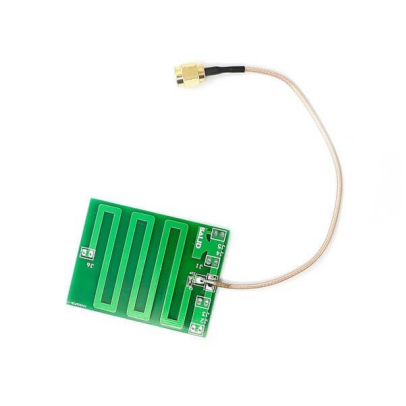

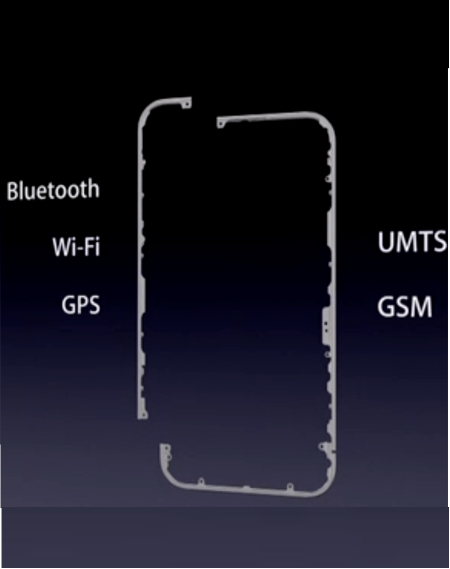
2. Flexible Printed Circuit (FPC) Antennas
Structure:
Thin flexible film with conductive ink patterns
Advantages:
✓ Lightweight and bendable
✓ Better radiation efficiency than PCB
✓ Easier to position in curved spaces
Disadvantages:
✗ Higher cost than PCB antennas
✗ Requires dedicated mounting space
✗ Less durable in extreme temperatures
Common Use: Main antennas in mid-range smartphones
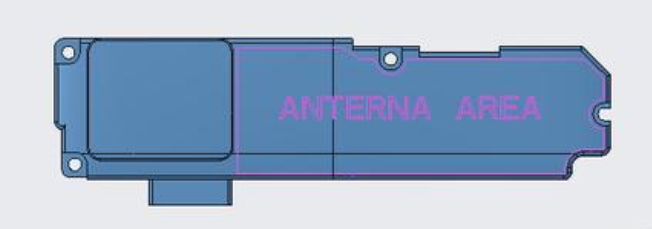
3. LDS Antennas (Laser Direct Structuring)
Structure:
3D plastic components with laser-etched metallic patterns
Advantages:
✓ Enables complex 3D designs
✓ Excellent space utilization
✓ Stable high-frequency performance
Disadvantages:
✗ Highest production costs
✗ Requires specialized manufacturing
✗ Longer development cycle
Common Use: Premium smartphones with millimeter-wave 5G

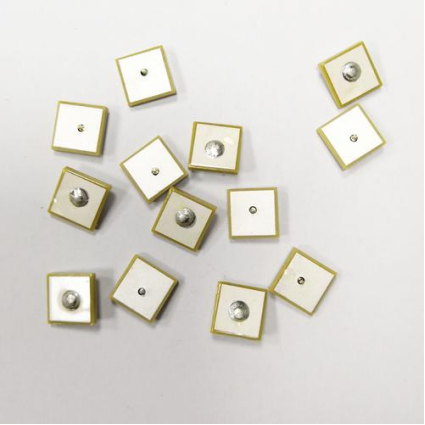
4. Ceramic Antennas
Structure:
Miniature dielectric ceramic components
Advantages:
✓ Ultra-compact size
✓ High thermal stability
✓ Low signal loss
Disadvantages:
✗ Narrow bandwidth
✗ Directional sensitivity
✗ Fragile physical structure
Common Use: IoT devices and smart wearables

5. Metal Frame Antennas
Structure:
Smartphone's metal chassis used as radiator
Advantages:
✓ Seamless visual integration
✓ Excellent heat dissipation
✓ Robust structural durability
Disadvantages:
✗ Complex impedance matching
✗ Hand grip interference
✗ Limited multi-band support
Common Use: Flagship phones with full-screen designs
Technology Comparison Table
Choosing the Right Antenna
Modern smartphones typically combine multiple antenna types:
√5G Devices: LDS + Metal Frame hybrid designs
√Foldables: Flexible FPC arrays
√Wearables: Ceramic + PCB combinations
As wireless standards evolve, antenna technologies continue to advance with innovations like:
√AI-driven beamforming systems
√Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) antennas
√Graphene-based transparent antennas
Contact our RF engineers to optimize antenna solutions for your next mobile device project.
AFU TELECOM is a Wireless Telecom Solution Expert with professional supporting on our customers' business globally. AFU TELECOM is always focusing on and specializing in O-RAN, Marco Cell, Small Cell, Active DAS, Public Safety and Optics Network Solutions including Antennas, Filters/Combiners/TMAs, RF Repeaters, Optics Devices and Site Accessories, especially AFU Core Team are very professional in Wireless Telecom with rich experience on our product portfolios. The Highest Priority of AFU TELECOM is Customers' Satisfaction and Product Quality. AFU MISSION IS TO CONNECT EVERYTHING!

